Structure of glass at high pressure
問い合わせ番号
SOL-0000001175
ビームライン
BL04B1(高温高圧)
学術利用キーワード
| A. 試料 | 無機材料 |
|---|---|
| B. 試料詳細 | 絶縁体・セラミックス, 非晶質、ガラス |
| C. 手法 | X線回折 |
| D. 手法の詳細 | 粉末結晶構造解析 |
| E. 付加的測定条件 | 高圧(大型プレス), 応力付加、変形, 高温(>>500度) |
| F. エネルギー領域 | X線(>40 keV) |
| G. 目的・欲しい情報 | 構造解析, 構造変化, 相転移 |
産業利用キーワード
| 階層1 | 半導体, 工業材料 |
|---|---|
| 階層2 | シリコン系半導体, 触媒, ガラス |
| 階層3 | ゲート絶縁膜, 層間絶縁膜, 容量膜 |
| 階層4 | 密度, 液体・非晶質構造, 原子間距離 |
| 階層5 | 回折 |
分類
A80.30 無機材料, M10.20 粉末結晶回折
利用事例本文
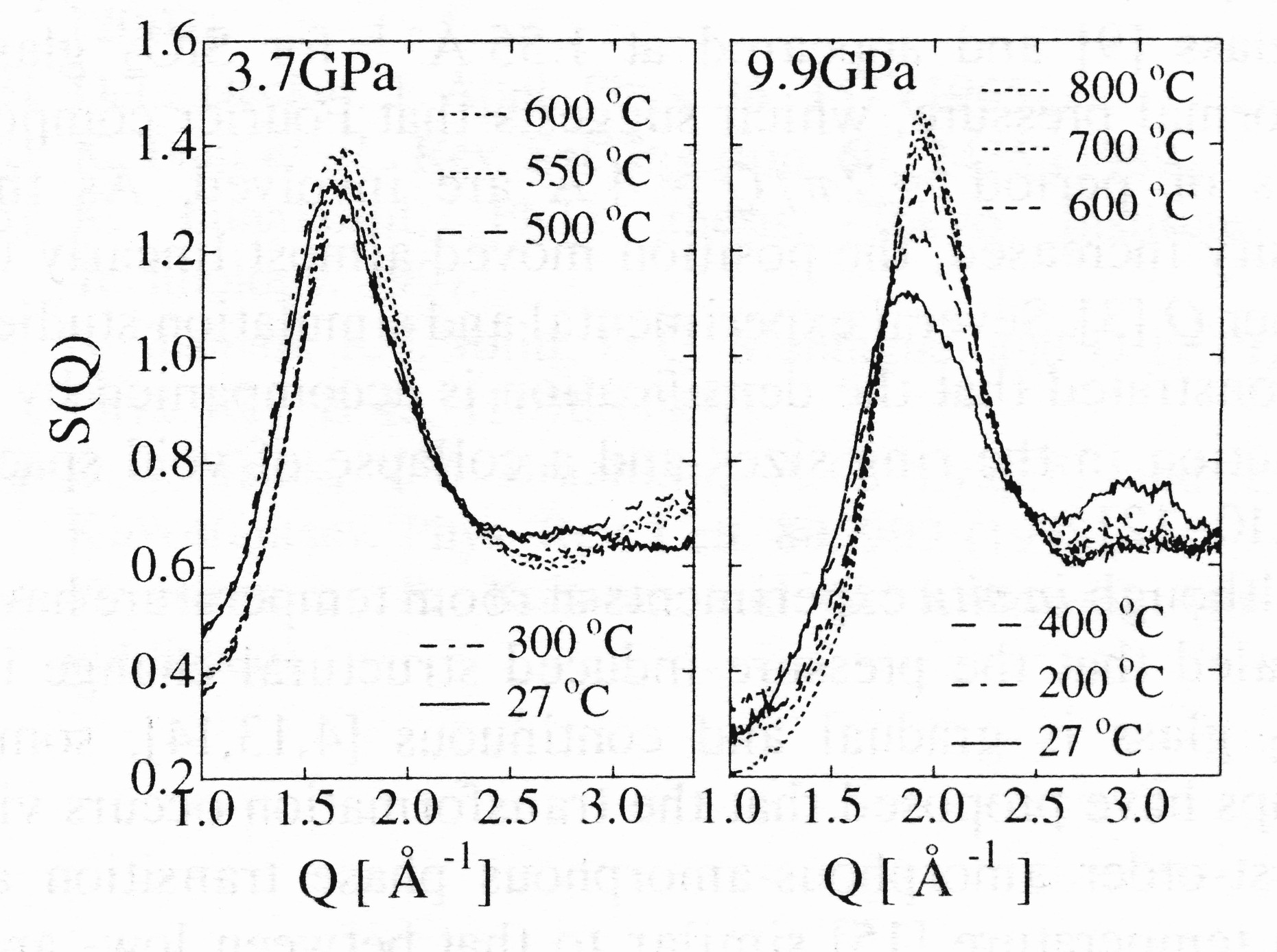
Different structures of SiO2 glass such as the highly densified glass have been recognized, but the existence of a first-order phase transition depending on the pressure and temperature is controversial. Energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction using a large-volume press, SPEED-1500 make it possible to observe the direct structure change of glass and melt under high pressure and high temperature. Figure shows the temperature dependence of the structure factor, S(Q) of SiO2 glass at 3.7and 9.9 GPa. The large increase in density is attributed to a significant modification in the intermediate range order, which is manifested by a drastic change in the first sharp diffraction peak (FSDP). The change of FSDP at 3.7 GPa is small, while a large change in FSDP is observed at 9.9 GPa with increasing temperature.The results indicate that there is a P-T region where the intermediate range structure relaxed to a denser one.
Fig. Temperature dependence of S(Q) of SiO2 glass at 3.7 and 9.9 GPa.
[ Y. Inamura, Y. Katayama, W. Utsumi and K. Funakoshi, Physical Review Letters 93, 015501 (2004), Fig. 3,
©2004 American Physical Society ]
画像ファイルの出典
原著論文/解説記事
誌名
Phys. Rev. Lett., 93, 015501(2004)
図番号
3
測定手法
An energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction system attached to the Kawai-type large-volume press is shown in figure. A white X-ray beam from the bending magnet light source is collimated with vertical and horizontal slits to form a thin beam possessing a cross section of typically 0.05 x 0.1 mm2. In order to carry out the energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction on the Kawai-type system, the first-stage anvils are cut holes to pass the X-ray beam. The incident white X-ray beam from the first-stage passes through the gaps between the second-stage anvils in a horizontal plane. X-rays diffracted by samples under high-pressure and high-temperature is detected by a pure Ge solid state detector (Ge-SSD) with a 4096 multi-channel analyzer. Diffraction data can be obtained with an energy range from 20 to 150 keV. Use of a collimator (0.05 mm width) and a receiving slit at a fixed angle to the direct beam permits only the diffracted X-rays from the sample to be detected. The horizontal goniometer covers a range of 2θ angles from -10 to 23° with an accuracy of 0.0001°. The X-ray acquisition time to obtain a diffraction profile is typically one to several minutes.
Fig. Schematic drawing of the energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction on the Kawai-type large-volume press.
画像ファイルの出典
BL評価レポート
ページ
14
測定準備に必要なおおよその時間
1 日
測定装置
| 装置名 | 目的 | 性能 |
|---|---|---|
| SPEED-1500 | High pressure and high temperature experiment | 2500K, 30 GPa |
参考文献
| 文献名 |
|---|
| Phys. Rev. Lett., 93, 015501(2004) |
関連する手法
アンケート
SPring-8だからできた測定。他の施設では不可能もしくは難しい
本ビームラインの主力装置を使っている
測定の難易度
中程度
データ解析の難易度
熟練が必要
図に示した全てのデータを取るのにかかったシフト数
4~9シフト